Imagine applying for a loan through a chatbot fast and intuitively, until you learn it denied your application. Why? It used ZIP code and gender as silent decision factors.
AI made the interaction possible. Ethical failure was harmful.
Today, AI powers critical decisions in HR, banking, healthcare, and online platforms. Without ethical design, these systems risk unfair exclusions and eroded trust.
This guide unpacks:
- What ethical AI truly means
- Why it’s essential for business, society, and legal compliance
- Real failures of unethical AI and how they happened
- Principles and frameworks for building responsible AI
- Tools, techniques, audit strategies, and governance models
Why Should You Care?
Let’s say you’re not a developer or AI researcher. Why should you worry about ethical AI?
Because AI already affects your daily life:
- Job applications screened by AI
- Banks using algorithms for credit scores
- Hospitals using AI for diagnosis
- Social media curating what you see
If the algorithms behind these systems are biased or opaque, they could reinforce injustice, misinformation, and even economic exclusion.
Insight💡: In 2018, a hiring algorithm at a major tech company Reuters was found to prefer male candidates over female ones for engineering roles. Why? Because it had been trained on resumes from the past mostly from men.
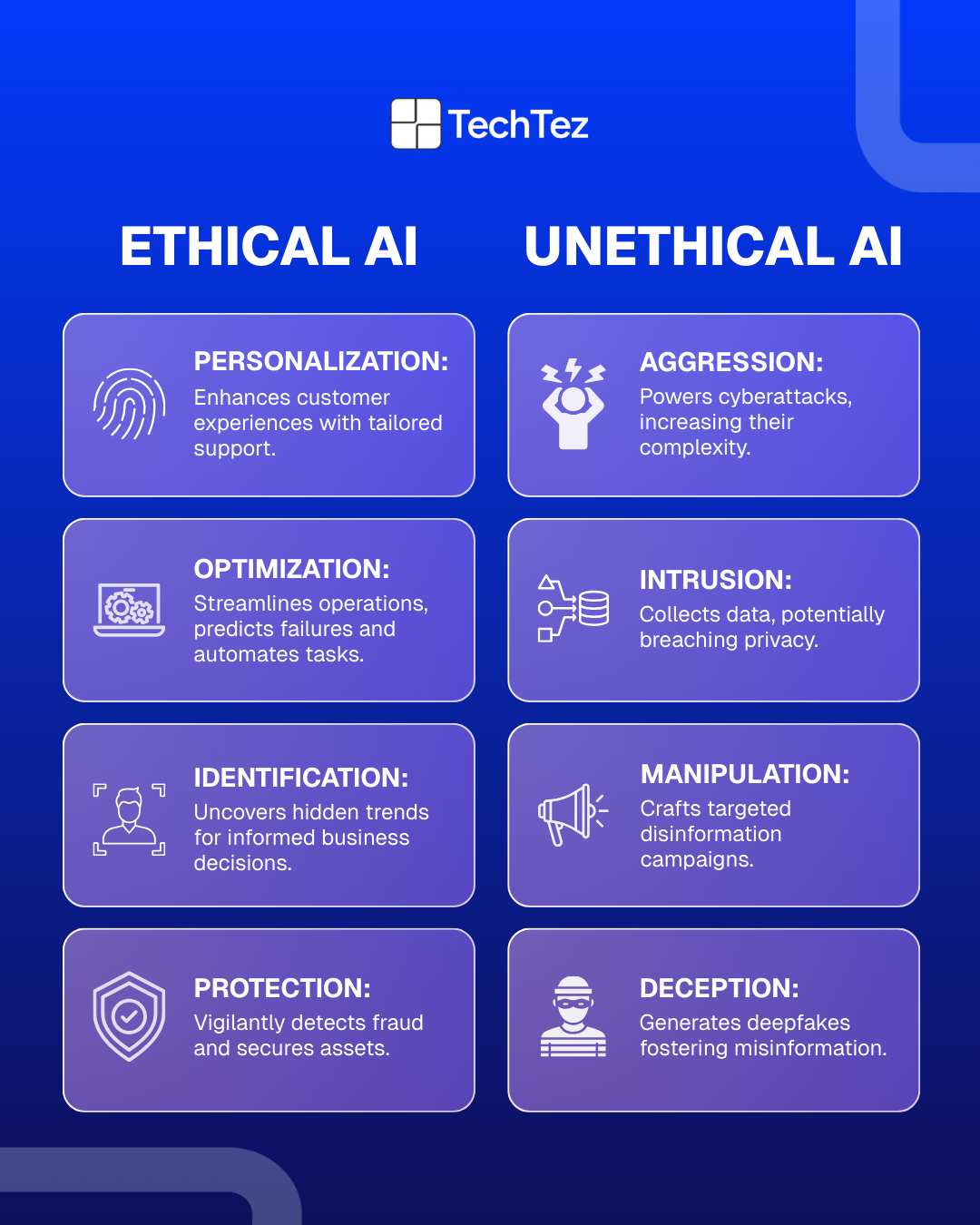
What Makes AI Unethical?
Unfortunately, AI doesn’t always play nice. Here are a few red flags:
- Bias in training data: If historical data is biased, AI will reflect that.
- Black-box algorithms: You can’t explain how or why it decided.
- Surveillance: AI used to monitor people without consent (e.g., facial recognition in public spaces).
- Weaponization: AI used in autonomous drones or cyberwarfare.
Insight💡: A 2021 report by UNESCO warned that without regulation, unethical AI could threaten human rights globally.
Why Businesses Are Embracing Ethical AI
It’s not just about avoiding lawsuits. Ethical AI = better business.
- Trust: Users are more likely to engage with ethical platforms.
- Compliance: Regulatory landscapes (like GDPR) are demanding AI transparency.
- Brand Reputation: Ethical companies attract top talent and loyal customers.
Insight💡: According to a 2023 PwC report, 86% of consumers said they would switch brands based on data ethics concerns.
Ethical AI in Everyday Life
Ethical AI isn’t just for big tech or governments. Here’s how it shows up around you:
- Google Search tweaking algorithms to fight misinformation
- LinkedIn using AI to reduce bias in job suggestions
- Apple offering privacy controls to let users’ control what’s tracked
Even AI artists, musicians, and storytellers are asking: Am I being inclusive? Am I fair?
Emerging trends shaping AI ethics in 2025 and beyond
I. Why Ethical AI Matters: The Stakes Are Real
A. AI’s Reach Across Life Domains
|
Domain |
AI Use Case |
Ethical Risk |
|
HR & Recruitment |
Candidate screening tools |
Bias against women, minorities |
|
Banking |
Credit scoring models |
Geographical and socio-economic bias |
|
Healthcare |
Diagnostic models |
Misdiagnosis or unreliable advice |
|
Social Platforms |
Algorithmic content feeds |
Polarization, invisibility of viewpoints |
|
Law Enforcement |
Predictive policing, surveillance |
Privacy violations, false positives |
B. Trust and Reputation at Risk
Algorithms aren’t innocent. Bias isn’t malicious but it’s impactful.
For example:
- A biased resume screening model can lock out talented women.
- A misconfigured content filter reinforces worldview echo chambers.
- Facial recognition misidentifies individuals from minority groups at higher rates.
In each case, technology falters not from complexity, but from design devoid of inclusive thinking.
C. Consumer & Regulatory Pressure
Survey: 86% of consumers would abandon a brand over AI/data ethics issues (PwC, 2023).
Regulation: The EU AI Act, California Consumer Privacy Act, and global AI ethics guidelines now demand accountability and transparency.
Ethical AI isn’t compliance alone it’s strategic risk mitigation and brand differentiation.
II. Defining Ethical AI: Principles That Protect & Empower
At its core, ethical AI is AI that’s transparent, fair, accountable, privacy-respecting, and safe.
A. Fairness
- Counter biased training data
- Use fairness-aware metrics (e.g. demographic parity, equal opportunity)
- Validate models with representative data sets
- Continual bias testing and remediation
B. Transparency & Explainability
- Use tools like LIME, SHAP to trace decisions
- Document model behavior, inputs, and known limitations
- Provide audit trails to technologists and users alike
C. Accountability
- Define decision ownership clearly
- Provide exception paths and human appeals
- Maintain governance logs and SLAs
D. Privacy, Consent & Data Protection
- Use data minimization and anonymization techniques
- Seek explicit informed consent with opt-outs
- Secure data storage and retention with auditability
E. Safety & Reliability
- Align models continuously with evolving policies or health guidelines
- Build model fallback and safe exit mechanisms
- Test thoroughly across adversarial and edge-case scenarios
III. Failures & Real-World Examples That Educate
1. Biased Hiring Platforms
An AI recruiter favoring male candidates due to biased resume history not policy or intent shut down high-skilled female talent pipelines.
2. Surveillance & Privacy Breaches
Unregulated facial recognition used to track public behavior without consent triggered international civil liberty controversies.
3. AI in Healthcare Misdiagnosis
AI systems lacking explainability or fallback can misdiagnose rare conditions—risking patient safety and litigation.
4. Financial Predatory Algorithms
Credit scoring models inadvertently excluded rural or low-income demographic groups by over-weighting ZIP-based risk factors.
These failures weren’t technical glitches; they were ethical oversights on the scale.
IV. Building Ethical AI: Roadmap for 2025
Step 1: Get the Team Right
- Bring together technologists, ethicists, legal counsel, engineers, and user advocates
- Diversity avoids blind spots and creates accountable systems
Step 2: Map Compliance Frameworks
- Use OECD AI Principles, EU AI Act, UNESCO AI Ethics
- Create organizational ethics boards and bias tags
Step 3: Model Development with Fairness & Transparency
- Use Fairlearn or AIF360 in model pipelines
- Use explainable model structures or post-hoc tools like SHAP/LIME
- Hard-code fairness thresholds where necessary
Step 4: Rigorous Data & Bias Audits
- Use fairness metrics and counterfactual testing
- Flag decision segments with high-risk demographic variance
- Run audits periodically post-deployment
Step 5: Privacy-Preserving Model Techniques
- Use federated learning, edge learning, or homomorphic encryption
- Implement differential privacy with noise addition where applicable
Step 6: Human-in-the-Loop Design
- Design decisions as assistive not automated especially in sensitive areas
- Maintain clear escalation paths and override capabilities
Step 7: User Transparency & Opt-Out
- Label AI outputs clearly (“AI-generated recommendation”)
- Provide clear data usage explanations and consent getters
- Allow users to appeal decisions or opt for human review
V. Tools and Governance Matrix
|
Area |
Tools / Practices |
|
Bias Detection |
Fairlearn, AIF360 |
|
Model Transparency |
SHAP, LIME, versioned audit logs |
|
Privacy Techniques |
Differential Privacy, Federated Learning frameworks |
|
Governance Frameworks |
OECD AI Principles, EU AI Act, UNESCO recommendations |
|
Oversight Mechanisms |
Decision review teams, SLA-led governance |
|
User Transparency |
Clear UI disclaimers, data usage policies, appeal interfaces |
These become the backbone of trusted, scalable AI deployment.
VI. Trends Dominating Ethical AI in 2025
- Regulation as Standard: Legal obligations like the EU AI Act and sectoral mandates for healthcare, finance, and education.
- Explainable AI is Non-Negotiable: SHAP, LIME, audit logs offer clarity across business and human feedback loops.
- Democratized Privacy Protection: Tools like federated learning allow collaboration without data pooling.
- Competitive Brand Impact: Ethical AI helps brands attract talent, win users, and avoid reputational damage.
- Human-AI Hybrid Systems: AI as advisor not decider especially in high-stakes or legacy contexts.
The Future of Ethical AI
The future of AI isn’t about robots taking over,it’s about humans and machines working better together.
Imagine:
- Doctors using AI that explains diagnoses in plain language
- Judges getting fairness scores on algorithmic risk assessments
- Students learning from AI tutors that adapt to their needs, not just the average
But none of this works unless we design with intention.
Final Thoughts: AI That Works for Us
Ethical AI isn’t another Trend, It’s the foundation of AI that respects people.
As we enter an AI-powered future, we must ask not just Can we build it? but also:
Should we build it this way?
Whether you’re a tech founder, developer, marketer, or user, knowing the basics of ethical AI empowers you to make better choices.
Because in the end, the smartest AI should also be the most human-centered.
Want to Learn More?
Need Help Building Responsible AI Systems?
At Techtez LLP, we help startups and enterprises integrate AI with ethical, secure, and compliant practices from model design to deployment.
Get in touch for a custom AI ethics audit or implementation strategy.